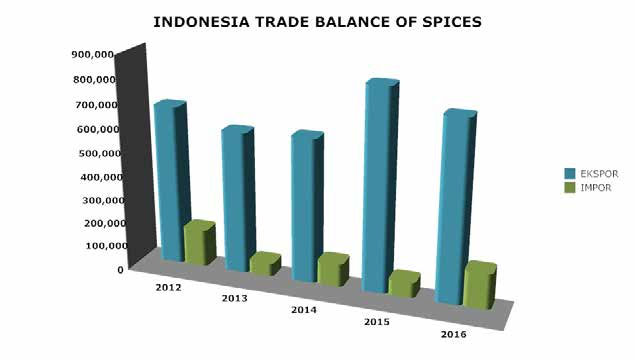
During the period of 5 years ie in 2012 to 2016, Indonesia plays a role of supplying about 14% of the needs of the world’s spices. Of that amount, about 79.4% of pepper products became the most exported commodities by Indonesia. Meanwhile, the next product is cinnamon which gives export contribution of 10%. It is impossible to determine the exact volume of spices produced in sustainability. Although the actual production figures provide a rough indication of organic crops, fair trade production data is not available. Rainforest Alliance spice production data is not available anyway, since the certificate was just introduced. Total domestic organic farming area of 8 million hectares (Ha) represents 0.14% of the total agricultural land of Indonesia. Organic agricultural sector is being intensively conducted by the government. Various efforts continue to be done in order to divert from conventional farming to organic farming. But there is still a bit of land that does the organic planting. Currently Indonesian farmers are still many who apply conventional planting system. With this planting system has side effects, such as farmers’ habits that often use pesticides with high levels, the frequency of pesticides are continuous in the short term and even some farmers are using the pesticide in flush instead of spray.
Understanding the value of Indonesia’s spice production in a global perspective provides a basic understanding to analyze the role of the country as a supplier to the international market. Spices is Indonesia’s fourth largest export commodity, after shrimp, fish and coffee. Pepper is the spice that has the most important role in this sector for the economic growth of Indonesia.
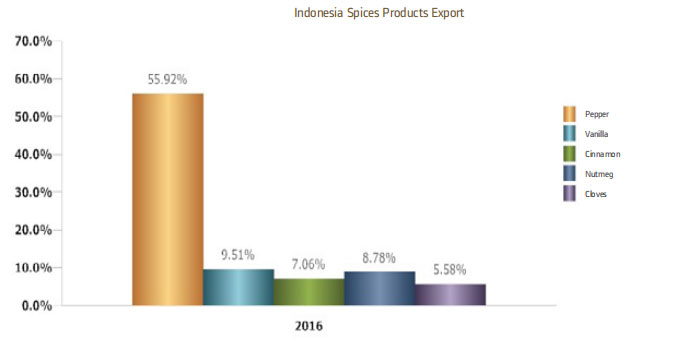
Indonesia’s pepper export in 2016 reached 51,759 tons and became the most exported commodity of Indonesia for spice category. By viewing the contribution of pepper exports is significant compared to other spices commodities that reach 55.9%. While other commodities such as vanilla only contributed 9.5%, cinnamon by 7.06%, Nutmeg 8.78%, Clove 5.58%. Vietnam became the largest export destination of pepper from Indonesia with export of 19,327 tons during 2016 or with export value of USD 122,4 million. The export value of pepper to Vietnam has a positive trend over the 5-year period from 2012- 2016 at 11.72%. Besides Vietnam, there is a United States of America which is the export destination of Indonesian pepper with total export of 8,540 tons. There are 5 provinces producing pepper commodities in Indonesia, including Bangka Belitung Islands, Lampung, South Sumatra, East Kalimantan, South Sulawesi. The islands of Bangka Belitung and Lampung are the main producers of pepper with its contribution to national production of 58.32 percent. South Sumatera, East Kalimantan and South Sulawesi provinces contributed 41.68 percent to national production.
The islands in the North Maluku Province cluster are the legendary sources of world cloves. Indian, Arab, Chinese and Javanese traders often come to Ternate, Tidore, and Banda which are the source of the world’s spices. They back home with the precious commodity to their home country for sale at a high price. Cloves, together with nutmeg and mace are so valuable in proportion to gold because they are used as a food spice and to preserve food or medicinal ingredients.
In addition, In Indonesia alone there are some areas that become producers of spices that have good quality, following areas that produce spices in Indonesia;
- Pepper. Lampung Province is the largest black pepper producing province. Many white pepper produced in Bangka Province. Other areas of pepper production are DI Aceh, Jambi, West Kalimantan,
East Kalimantan, Lampung, West Nusa Tenggara, South Sulawesi, Southeast Sulawesi, South Sumatra, North Sumatra, and Yogyakarta. - Cloves, Maluku Province is the largest producer of cloves. Other producing regions are North Sulawesi, Aceh, West Sumatra, Lampung and Central Java.
- Nutmeg is the number two commodity of the VOC era. Producing areas of nutmeg, such as Bengkulu, Maluku, Papua, South Sulawesi, Southeast Sulawesi, and North Sulawesi.
- Ginger, warmth of ginger is very famous in Continental Europe. Ginger can flourish in all areas.
- Cinnamon, are found in Jambi, West Sumatera and Yogyakarta.
- Onion, in Indonesia is currently the largest producer of red onion in the area of Brebes Regency, located in Central Java Province. Other areas are West Kalimantan and South Kalimantan.
- Pecan, producing areas of candlenut such as Mamuju West Sulawesi Province, Sigi District, Central Sulawesi, Bima West Nusa Tenggara Province.
- Cardamom is produced primarily commercially produced from West Java and southern Sumatra.
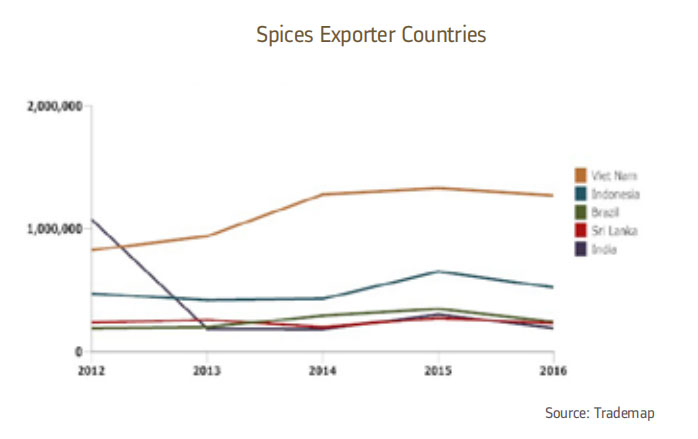
In the development of world spice trade, Indonesia is still ranked second after Vietnam as a spice exporter. Indonesia’s export value fluctuated during the 5-year trade period between 2012 and 2016, had a significant increase in 2015 with a value of USD 652.24 million compared to the previous year’s value of only USD 430.91 million.
However, in 2016 the value of Indonesian exports again decreased at USD 524.29 million. Nevertheless, Indonesia’s export value still has a positive trend during that period of 6.67%. Indonesia actually has great potential to master the spice market of the world, one of the efforts that can be done to improve the competitiveness and promotion of exports of selected herbs is to develop geographical indications (IG). Given Geographical Indications, the herb farmers are expected to benefit tremendously.